What is the difference between PCB and FPC?
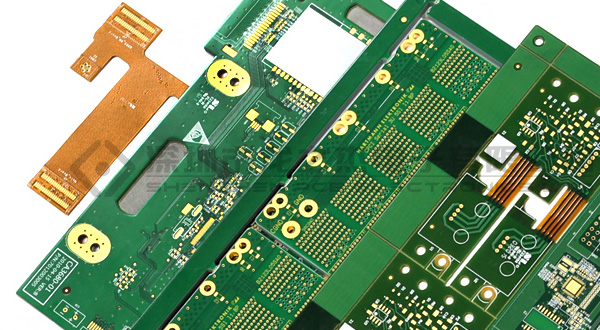
Firstly, FPC and PCB have different materials. FPC uses flexible substrates, usually polyester film or polyimide film, which have high flexibility and toughness. In contrast, PCB substrates are usually made of glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin (FR-4) or metal substrates, which are more rigid and sturdy.
Secondly, FPC and PCB have different characteristics. FPC has excellent flexibility and bending performance, which allows it to bend and fold in three-dimensional space. Therefore, FPC is usually used in applications that require high reliability and flexibility, such as mobile devices and medical equipment. In contrast, PCB is usually rigid and two-dimensional, making it suitable for applications that require lower costs and higher performance, such as computers and electronic devices.
Thirdly, FPC and PCB have different applications. In addition to the applications in mobile phones, tablets, handheld devices, automotive electronics, and medical equipment, FPC can also be used in applications that require compact design, such as cameras, LED light strips, and smart bracelets. In contrast, PCB is usually used in applications that require lower costs and higher performance, such as computers, televisions, audio equipment, and other electronic devices.
Finally, FPC and PCB also differ in the manufacturing process. FPC usually uses flexible substrates, so different manufacturing processes are required. For example, in the FPC manufacturing process, a drilling machine is used for hole processing, while in the PCB manufacturing process, a CNC drilling and milling machine is used for hole processing. In addition, the chemical reagents and process flows used in the FPC manufacturing process are different from those used in the PCB manufacturing process.
In conclusion, FPC and PCB are two common types of printed circuit boards. They have differences in materials, characteristics, and applications. FPC has excellent flexibility and bending performance, making it suitable for applications that require high reliability and flexibility, such as mobile devices and medical equipment. In contrast, PCB is usually used in applications that require lower costs and higher performance, such as computers and electronic devices. Choosing the appropriate printed circuit board type is essential in PCB assembly and can improve the reliability and performance of electronic products.

